In my recent posts I have reported of my fieldwork for our EU-funded TACCLE4-CPD project. The aim of this project is to develop training models and pedagogic approaches to promote digital competences of teachers and trainers in different educational sectors. In my blog posts I have mainly emphasised the specific characteristics of my work that focuses on the field of vocational education and training (VET). With this series of posts I will try to link my work to the general framework of the project and to the work of other partners in other educational sectors (general education, adult education) and with school-based learning. The starting point is provided by the Four-Step Model that was developed in the recent project meeting in Bucharest (in which I couldn’t participate). In this first post I will present the outline of the model (as it was explained to me afterwards) and how it can be applied in schools and adult education providers. In the subsequent blogs I will discuss, how the model can be adapted to the field of VET and to my recent findings in the fieldwork.
The Four-Step Model for finding/developing strategies to promote digital competences
The Four-Step Model for finding/developing strategies was shaped in the project meeting in Bucharest, when the TACCLE4-CPD partners had workshops with interested schools. When analysing the experiences of the workshops the partners came up with the model that is visualised below.
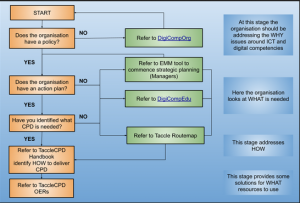
Figure 1: The Four-Step Model for finding/developing strategies to promote digital competences in educational contexts (credit to Graham Attwell and Angela Gerrard)
As we see, the left hand side presents the process steps with key questions and related options, how to proceed. In the middle we see the reference materials that can be used in the process. And on the right hand side we see the underlying questions that clarify, where the questions and answers lead us.
My interpretation of the four-step model (as it stands now)
As I read this model, it speaks out to school managers, educational authorities and curriculum developers. They are challenged to consider, whether their organisation(s) is/are following a policy for promoting digital competences. In this respect they are advised to inform themselves of the European DigCompOrg frameworks (prepared by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Union). In the next phase they are challenged to consider their strategic approach in terms of action plans and needs analyses. Here they are advised to have a closer look at the DigComgEdu framework (also by JRC) for specifying their strategic orientation. Then, in the next phases the model invites to discuss, how continuing professional development (CPD) can be organised and delivered. Here the model refers to earlier TACCLE resources (Routemap) and to the new Handbook that is being prepared for the TACCLE4-CPD.
—
As I see it, this model suits very well school-based educational contexts. However, when we discuss the field of VET, we are dealing with a more complex policy environment and institutional/organisational landscape. Moreover, we are dealing with diversity of learning venues (schools, enterprises, intermediate training centres) and with domain-specific characteristics (different occupational fields, different production and service contexts). Therefore, it is appropriate to discuss the Four-Step Model in the light of these challenges. That is the task for my next blog post in this series.
More blogs to come …

