 This is a new paper, written by Graham Attwell and Ana Garcia about the new apprenticeship system in Spain. The research was sponsored by the International Network on Innovative Apprenticeship (INAP) and the paper will be presented at the “Crossing Boundaries in VET: Social Dimension and Participation” conference in rostaock in August. We will provide a downlaodable version of the paper once we have overcome our fight with Word templates.
This is a new paper, written by Graham Attwell and Ana Garcia about the new apprenticeship system in Spain. The research was sponsored by the International Network on Innovative Apprenticeship (INAP) and the paper will be presented at the “Crossing Boundaries in VET: Social Dimension and Participation” conference in rostaock in August. We will provide a downlaodable version of the paper once we have overcome our fight with Word templates.
Abstract: This paper, explores the outcomes of a short action research project, undertaken in Valencia Spain in 2016, into the introduction of the new apprenticeship qualification, FP Dual. The hypothesis underpinning the work was that the development of apprenticeship programmes in Spain needs to build on existing cultural and organisational norms and requires an in-depth understanding of critical factors in the perception of apprenticeship by different actors. The research was undertaken through a series of over 30 in depth interviews with different actors. The paper explains the background and methodology, before outlining the major issues that emerged from the research. The conclusion suggests the need to address cultural and educational issues that the introduction of a Dual System system raises, including the relations between companies and education institutions, the prestige of vocational qualifications, the training of teachers and trainers and issues of pedagogy and curriculum.
Keywords: Action research, Semi structured interview, Apprenticeship, Policy, Spain
1 Introduction
The Spanish economy is still struggling from the impact of the ‘crisis’, with persistently high levels of youth unemployment and low skills levels. Unemployment is especially high for those leaving school early with no qualifications and for recent graduates (Esenciales Fundación BBVA, 2016).
A series of reports have suggested that moving beyond the school based, initial vocational training system to adopt a dual system based, apprenticeship model offers benefits to the economy, to companies and to individuals (Wolter and Mühlemann, 2015).
However, other research points to the difficulties in transferring models developed in one culture – such as the German Dual apprenticeship system – to other cultures such as Spain (Pilz, 2016). These include the weakness of trade unions at a company level, educational polarisation between vocational and higher education, resistance at company level, resistance by families and young people, variation in co-ordination between actors from region to region, complex interactions between national and regional levels, the government, social partners and employment organisations and, of course, the ongoing economic crisis (Cedefop, (2015).
The Spanish government has established an experimental apprenticeship framework, FP Dual, with pilots running in parallel to existing VET schemes (Refer Net Spain, 2014). The implementation of the programmes varies greatly in different Autonomous Communities, based on different cultures, different economies and different organisational and governance forms.
Clara Bassols and Guillem Salvans (2016) say that the Spanish FP Dual system is underdeveloped and needs to be refined and improved to ensure that it is genuinely capable of providing young people with the necessary professional skills and thus employability. Comparing developments in Spain with the German Dual apprenticeship training system, they say that while the two Dual VET systems will never be the same, comparison with Germany reveals that the Spanish system lacks some of the defining strengths of the German system. That the Spanish Dual VET system is so new is viewed as “an opportunity to make changes before it becomes too entrenched.”
Our hypothesis is that the development of apprenticeship programmes in Spain needs to build on existing cultural and organisational norms. This requires an in-depth understanding of critical factors in the perception of apprenticeship by different actors and how these affect the development and implementation of apprenticeship programmes.
The ‘Understanding cultural barriers and opportunities for developing new apprenticeship programmes’ project, sponsored by INEP, has undertaken a four-month research study based in Valencia, to explore the cultural and organisational norms and the barriers and opportunities these afford to introducing apprenticeship. In this paper, we explain the methodology behind the research and the main findings.
2 Research Methodology
A key aim for the project was understanding the introduction of an education innovation – apprenticeship – within a local setting and with a wide range of different actors.
The project adopted an action research approach. Our aim was to develop an understanding of the underlying causes of issues relating to the introduction of educational practice in order, in the longer term, to arrive at consensus by different social partners on how practice can be improved. Our focus has been on qualitative research with different actors who may have an important voice in this area, the organisation of apprenticeship, the role of different organisations and the cultural factors affecting the provision and reform of vocational education and training in the Valencia Community and in Spain.
Elden (1983) has introduced the notion of ‘local theory’. To understand the challenges of each specific workplace, he said, as well as how to attack them, there is a need to understand this specific workplace. In a similar way, we would suggest the need to understand the specific ideas and activities and ‘theories’ of different actors involved at a local level in apprenticeship. Here theory might be understood as the specific pedagogic and learning approach of apprenticeship in bringing together vocational training within schools with alternance periods spent within companies. One objective for our research was how such theory is linked to practice in introducing and supporting such programmes.
In the first stage of the project, we identified the major actors involved in the development and introduction of the apprenticeship programmes in Valencia. These included:
- Vocational Training Schools (directors, teachers, tutors)
- Policy Makers (regional government and political parties and organisations)
- Students and trainees
- Parents and carers
- Companies especially Small and Medium Enterprises.
The project adopted the idea of purposive sampling for selecting respondents for interviews (Patton, 1990). Interviews were conducted face-to-face using semi structured questionnaires. Overall, thirty interviews were conducted, recorded and transcribed.
3. Findings
In line with our approach to the project, we present here detailed findings from te different actors involved in developing apprenticeship at a local city level.
The role of companies in the FP Dual
Given the central nature of companies to the FP Dual system, it is not surprising that the relationship between companies and vocational schools, as well as the local administration was a major issue raised by all the different social partners. Although most company representatives interviewed were positive about the FP Dual and vocational schools welcomed the partnership with companies, it is proving time consuming to develop a culture and processes to support a dual system and the number of apprenticeship programmes and the number enrolled in Valencia remains limited. There are particular difficulties involving SMEs, who are reluctant to contribute to the cost of apprenticeship and lack skilled trainers.
The role of the school centres
Despite the support of some large and important companies, the adoption of FP Dual is being driven by the School Centres. In such a situation, it is possible that the large integrated centres are in a better position to lead such development, although this is not to downplay the contribution and effort of the smaller centres. School leadership is a critical factor, as is the commitment and contribution of teachers in the vocational schools. Directors and teachers receive no remuneration to working with companies to develop new programmes.
Administration and Contracts
The bureaucracy associated with the establishment of new apprenticeship programmes, both for the schools and for the companies, is troubling.
Some Autonomous Communities have legislation on contracts and remuneration for apprentices with differing rulings. In Valencia, it depends on the individual programmes negotiated between the company and the vocational schools. Quite obviously, this is problematic in that some apprentices are being paid for their work at the company while others are not. Furthermore, some apprentices, who are not receiving remuneration from the company, may be incurring some considerable expenses for travel.
Curriculum Design
At present, the FP Dual programmes last two years in contrast to the normal three-year length of apprenticeships in the German Dual system. There is concern that a some subjects, the curriculum is too heavy for such a time and there is a need for rebalancing drawn between what is learnt through the school and through in-company training.
Sector organisations
One key factor in implementing the FP Dual, is the strength and support of sector organisations which varies between different sectors. The initial programmes are being implemented where there is good communication and support between sectors, vocational schools and industries.
Flexibility and collaboration
The flexibility for the Autonomous Communities to implement apprenticeship schemes allows programmes to be adapted and planned according to the needs of local economies and societies. This may be a problem in terms of transferability of different courses and in transparency of what apprenticeship programmes stand for. There is an important balance to be achieved between the design of programmes to cater for the needs of individual companies and more standardised curricula which meet the needs of students in their education.
Careers guidance and the role of parents
There is only limited public awareness of the FP Dual and the aims and the organisation of apprenticeship. This issue is particularly salient given the high prestige placed on academic courses in Spain and particularly university programmes within the wider Spanish society. The weakness of education and guidance networks and services within Valencia is a major issue if young people, and especially higher achieving young people are to be recruited on FP Dual programmes and if companies and SMEs are to understand the value of apprenticeship.
Initial training and Professional development
There is a lack of a dedicated and well organised and resourced programme of professional development for vocational teachers and for trainers in companies, which is seen as a pre-condition for the future success of apprenticeship in Valencia. Initial training for vocational school teachers is overly focused on the subject with too little attention to pedagogic approaches to teaching and learning.
Sharing resources and good practices
The vocational schools appear to have well developed unofficial networks. But more formal networks are needed which could generalise discourses over strategies and approaches to apprenticeship and provide a forum for knowledge development and exchange.
There is a general concern that vocational education lack prestige, but more importantly the vocational centres often lack sufficient resources to not only maintain present programmes but to develop apprenticeship. This is linked to their understanding of the need for recognised quality in teaching and learning if apprenticeship is to succeed. Many teachers said they lack resources and there is poor access to technology.
International collaboration
European projects and programmes, including the development of new curricula and qualifications, new pedagogic approaches, the use of new technologies and the exchange of students and teachers are extremely valuable for vocational schools to develop and exchange knowledge and experience about apprenticeship.
Regional and city wide collaboration
Vocational schools appear to be approaching companies individually. There could be gains through developing more formal and extended networks between schools and companies, either on a regional or a sector basis. To an extent this role is being undertaken at a national basis by the Alliance for Apprenticeship. The establishment of the Alliance at the level of the Autonomous Communities could be an important step in promoting the FP Dual.
FP Dual and the local economy
Many of those interviewed saw apprenticeship as a way of proving the skills which the local economy would need in the future, particularly in view of the potential flexibility in designing new programmes together with employers. However, they also recognised the challenges in developing such a responsive system.
Evaluation
The new apprenticeship programmes are experimental, and many of the issues arising are not unique to Spain. Indeed, many of these issues have been raised in research into the long established German Dual System. However, the lack of qualitative evaluation of the FP Dual programmes, especially scientifically undertaken and published case studies, is a barrier to understanding what is working, what is not and how to improve the quality of the programmes.
4. Conclusions
The findings from this research are focused on the context of educational change and introducing apprenticeship in one community, Valencia in Spain. This raises the question of how generalizable they are to other regions and other countries. We would suggest the findings show the limitation in attempting to transfer models of vocational education and training from one country to another. Inevitably, FP Dual reflects the governmental, cultural, pedagogic and curricula history and practices of Valencia, as well as the particular context of the ongoing economic crisis. That does not mean that developing an apprenticeship system in Valencia is either undesirable or impossible. But it does mean going beyond lauding the strengths of dual system approaches to education and training and whilst recognising that a Dual system in Spain will always be different to Germany, addressing some of the cultural and educational issues that such a system raises. These include the relations between companies and education institutions, the prestige of vocational qualifications, the training of teachers and trainers and issues of pedagogy and curriculum. Announcing a new systemic innovation alone is not enough: unless these key issues can be addressed apprenticeship will not succeed in Valencia or in Spain.
References
Bassols, C. and Salvans, G. (2016). High Quality Vocational training in Spain: the Alliance for Dual Vocational training, Bertelsmann Foundation, Madrid
Cedefop (2015). Governance and financing of apprenticeship, Cedefop, Thessaloniki
Elden, M. (1983). Democratization and participative research in developing local theory. Journal of Occupational Behaviour, 4(1), 21–34.
Esenciales Fundación BBVA (2016). La formación ha avanzado durante la crisis, peroel abandono escolar, los desajustes en competencias y el paro limitan el aprovechamiento del esfuerzo educativo, Ivie N.º 03/2016
Patton, M. (1990) Qualitative evaluation and research methods. (pp. 169-186), Sage Publications, Beverly Hills, CA
Pilz, M. (2016). Training Patterns of German Companies in India, China, Japan and the USA:What Really Works?, International Journal for Research in Vocational Education and Training (IJRVET), Vol. 3, Issue 2, August 2016, pp. 66-87
Refer Net Spain (2014) Apprenticeship-type schemes and structured work-based learning programmes: Spain, CEDEFOP
Wolter, C. and Mühlemann, S. (2015) Apprenticeship training in Spain – a cost effective model for firms?, Bertelsmann Stiftung, Guetersloh
 Two weeks ago, I bought a new television. The old one had served well for 15 years but pre-dated the internet integration that we all take for granted these days. I carefully untangled the cables joining the various boxes with their flashing lights and plugged them back in again.
Two weeks ago, I bought a new television. The old one had served well for 15 years but pre-dated the internet integration that we all take for granted these days. I carefully untangled the cables joining the various boxes with their flashing lights and plugged them back in again. -Stiftung,
-Stiftung, 
 don’t have the money to pay for fees and travel (let alone beer) in attending these events. I am not sure that I actually miss the conferences themselves, but I do miss meeting friends and catching up with what is going on.
don’t have the money to pay for fees and travel (let alone beer) in attending these events. I am not sure that I actually miss the conferences themselves, but I do miss meeting friends and catching up with what is going on.


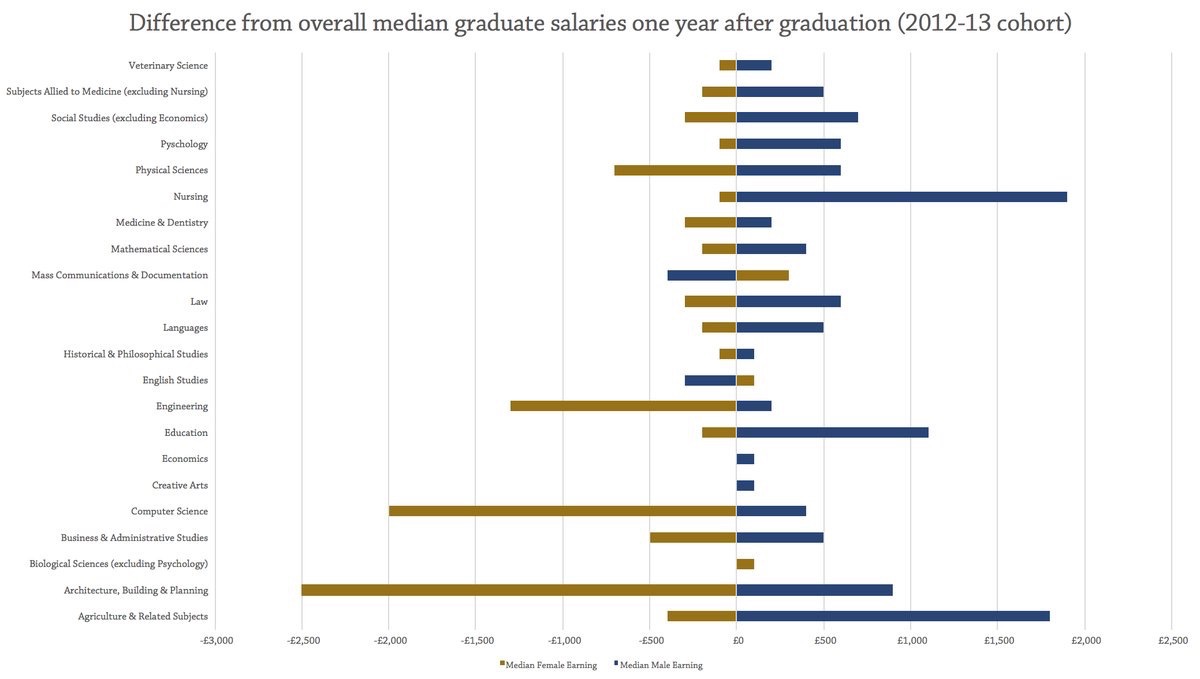
 This is a new paper, written by Graham Attwell and Ana Garcia about the new apprenticeship system in Spain. The research was sponsored by the International Network on Innovative Apprenticeship (INAP) and the paper will be presented at the “Crossing Boundaries in VET: Social Dimension and Participation” conference in rostaock in August. We will provide a downlaodable version of the paper once we have overcome our fight with Word templates.
This is a new paper, written by Graham Attwell and Ana Garcia about the new apprenticeship system in Spain. The research was sponsored by the International Network on Innovative Apprenticeship (INAP) and the paper will be presented at the “Crossing Boundaries in VET: Social Dimension and Participation” conference in rostaock in August. We will provide a downlaodable version of the paper once we have overcome our fight with Word templates.
