As usual, I have also this year participated in the European Conference on Educational Research (ECER). This year the conference was organised in Bolzano-Bozen – in the bilingual South-Tyrolean area next to the Dolomites. But for me and my colleagues this was not at all a touristic mission. In addition to the ordinary conference program we were in charge of the pilot activities with ePosters powered by the Learning Toolbox (LTB). In my previous post I have reported on our preparatory activities. Now it is time to report, how we put it all into practice and what kind of experiences we made. Below I give first insights into the Interactive ePoster session of the VETNET network (European Vocational Education and Training Research Network). Then I report on the EERA special session for discussing the use of the new toolset – the LTB – for preparing ePosters in a wider context.
The Interactive Poster Session of VETNET with ePosters presented in a session room
As I have reported in my previous post, we had invited all authors who had proposed posters to be presented in the VETNET (Network 2) program of the ECER 2018 to prepare ePosters and to present them in an Interactive Poster Session in the VETNET area. We were pleased that all authors had agreed and that we had their ePosters ready in the EERA showcase prepared by the LTB developers. However, we had very little advance information on the venue and very little time to prepare the room for the session. Thus, the best we could do was to organise a similar session as an ‘ordinary’ paper session – but now presenting ePosters. A major difference, however, was the fact that we had a full set of mini-posters presented on ‘poster wall’ in the session room before the session and it remained after the session.

Mini-posters for the VETNET ePoster session at ECER 2018
We had an additional difficulty in the fact that the EERA session was scheduled immediately after the ePoster session, so we had to organise the presentation and discussion on six posters in a tight time frame to get in time to our next session. For this purpose we grouped the presentations into pairs that had some commonality in their themes. Here again, our authors were flexible and the arrangement suited them.
Firstly. Wilko Reichwein presented insights into the cross-university cooperation in shaping vocational teacher education by linking subject disciplines and pedagogic know-how to each other. Then Marta Virgós Sánchez provided insights into the implementation of ‘dual’ training models in Spain. Cooperation between learning venues (Lernortkooperation) was discussed from the perspective of educational planning (the German presentation) and from the perspective of feedback from the parties involved (the Spanish presentation).
Secondly, on behalf of a Hungarian research team Marta Takacs Miklósi and Attila Karoly Molnar presented their comparative studies between the preconditions for education, training and learning in the prisons in Hungary and Poland. Then they presented insights into the learning opportunities and the role of andragogy (adult-oriented support for learning) in Hungary and Slovakia.
Thirdly, Maria Christidis gave insights into the communication culture and learning culture within the training of nurse assistants in Sweden. Then Katharina Peinemann provided insights into the inclusion issues in the German pre-vocational learning provisions (the ‘transitional system’ ) and into challenges for teachers’ professional development.
Altogether, we suffered from the time constraints, but we could stimulate some discussion. And since the authors could stay a little longer at the ‘poster wall’, they could advise interested participants, how to upload the richer LTB stacks (with the help of the QR-code) to mobile phones and get further information.
The special EERA session “Using Learning Toolbox for presenting Educational Research”
Our next session – the EERA-wide event to inform participants from other networks on the ePosters and the LTB – had been proposed and planned before we knew how successful we would be with the VETNET session. Therefore, we had planned firstly a presentation that gives a report on the development of the LTB in the Learning Layers (LL) project. This was prepared by me. (I will get back to this input in my next post.)
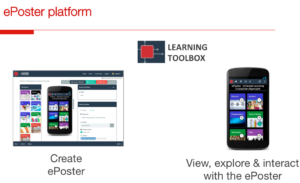
How to start with ePosters – extract from Gilbert’s presentation
The main input for this session was prepared by Gilbert Peffer on behalf of the LTB-developers. He gave insights into the functioning of the LTB, on the process of preparing and presenting ePosters and on possible uses of ePosters at different conference venues. Also, he presented newer ideas for developing ePoster sessions, e.g. the ePoster Arena. (This includes a central podium for presenting several short pitches and then distributed round tables for discussions with presenters.)

New engagement formats – extract from Gilbert’s presentation
In the discussion we had feedback from the authors of the VETNET ePoster session and further questions from representatives of other networks. Also, we got several questions concerning the use of LTB as support for practice-based learning in vocational and higher education. We still have a lot of impressions to digest and a lot of points to be made to EERA as conclusions on our pilot project.
—
I guess this is enough of this pilot project. But I will keep the topic ‘ePosters’ present when I give an account on my own presentations. I also did my homework in preparing ePosters although I presented in somewhat different sessions.
More blogs to come …





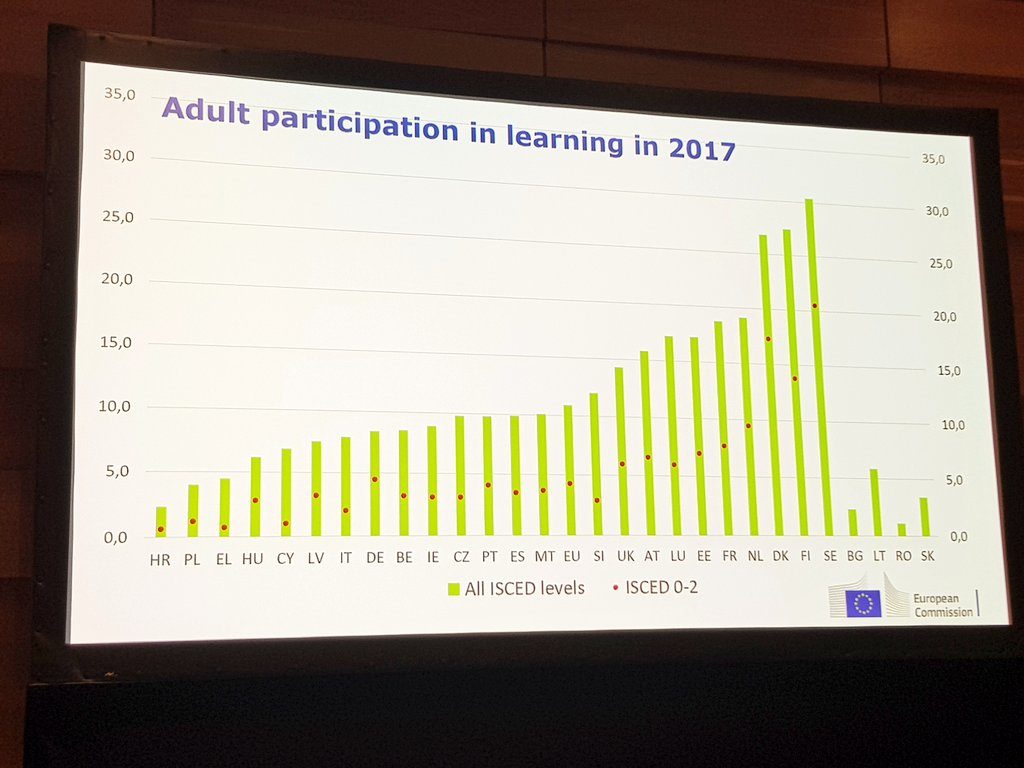 I am ever more interested in the issue of data literacy and agree very much with Javiera Atenas from the Open Education Working Group, London
I am ever more interested in the issue of data literacy and agree very much with Javiera Atenas from the Open Education Working Group, London