Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the EU CONNECT project. Funded under the Erasmus Plus programme, the CONNECT project aims to leverage the impact of Learning Cities through building urban ecosystems of lifelong learning that harness the assets of European cities and transform them into a network of seamless pathways of learning experience for adult learners. The project application says: “In a society where existing educational pathways no longer guarantee opportunity, and with a growing gap between the haves and the have-nots, connected learning for all citizens can open up new entry points and pathways to opportunity; in particular when integrating both the potential of ubiquitous learning technology and learning opportunities created by European cities.”
Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the EU CONNECT project. Funded under the Erasmus Plus programme, the CONNECT project aims to leverage the impact of Learning Cities through building urban ecosystems of lifelong learning that harness the assets of European cities and transform them into a network of seamless pathways of learning experience for adult learners. The project application says: “In a society where existing educational pathways no longer guarantee opportunity, and with a growing gap between the haves and the have-nots, connected learning for all citizens can open up new entry points and pathways to opportunity; in particular when integrating both the potential of ubiquitous learning technology and learning opportunities created by European cities.”
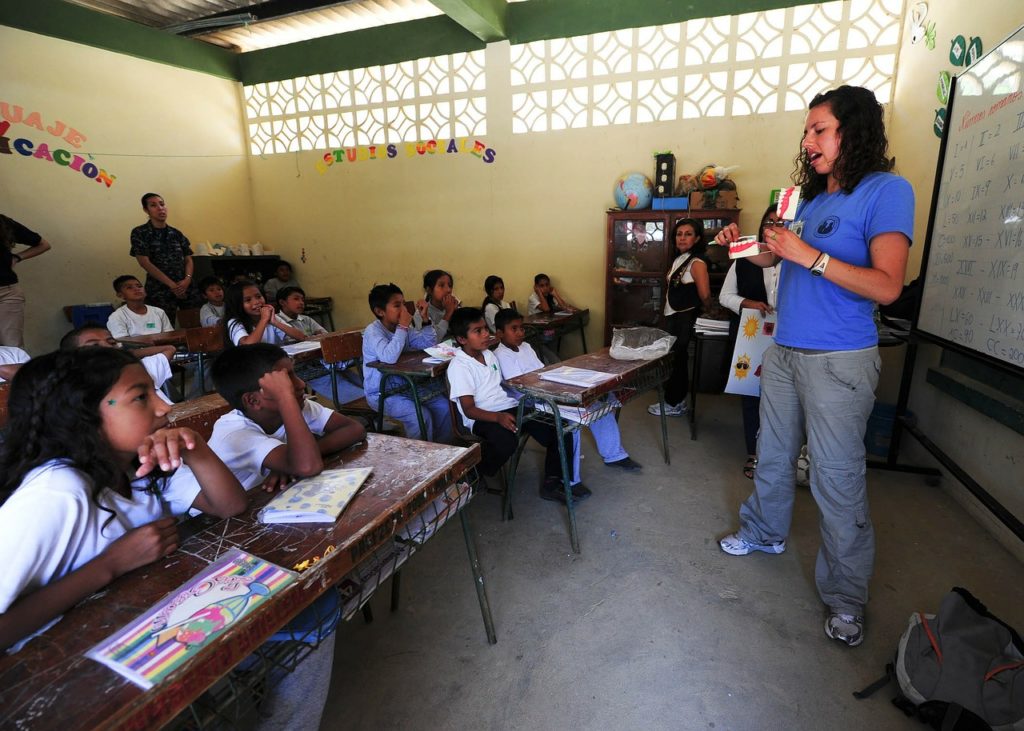
Pontydysgu have been working on two main things. Firstly, we have been doing a field study on Russafa, an area of Valencia, looking at different opportunities for non formal and informal learning, as well as at formal adult learning provision. One of our main conclusions is the importance of public spaces for learning to take place. To this extent history, culture and context play an important role and not least climate: in Valencia many learning opportunities take place outdoors! Urban design is another key contextual factor.
Secondly, we have been undertaking a literature review. One of the most interesting documents we have come across is ‘Cities of Learning in the UK’ – a “prospectus” published by the RSA. Cities of Learning (CofL), they say “is a new approach for activating a grassroots, city-based, mass engagement movement around learning and skills. It seeks to close gaps in opportunity and empower places to promote lifelong learning as core to their cultural and civic identity.”
“CofL can be a galvanising force for bringing people together with a city’s economic and social aspirations. It can open new sources of city leadership, learning potential and civic energy. Cities can both make visible and amplify nascent systems of learning – involving learners, institutions, employers, civil society and the voluntary and cultural sectors. Learners, especially those from underserved communities, can benefit from much greater access to the wealth of enrichment experiences and opportunities their city offers. By deepening social and civic connections, CofL can be a means to developing a sense of place, identity, mission, ambition – and learning.”
The Cities of Learning movement started in the USA but the Prospectus has been “adapted for UK.”
One thing I very much like about the CofL approach is the emphasis on place. As the RSA say “Learning systems – formal, non-formal, informal – are experienced by people in places and form a fundamental part of how they experience life within their neighbourhoods, communities, and towns and cities. They operate outside of the silos of traditional programmes, allowing organisations to work together to focus on shared outcomes rather than individual concerns.”
They go on to say that CofL “capitalise on crucial intangible factors that drive collective action, such as identity, heritage and community.” Certainly, from our research in Valencia we would concur – although I am not sure that heritage and community are intangible.
The Prospectus emphasises the widening participation and opportunity gap in society today.
It stresses the importance on non-cognitive as well as cognitive skills for future employment. Skills and calls for cities to develop learning pathways leading to Open Badges, recognizing learning or formal and informal learning experiences. Learning networks would incorporate a skills spine using both OECD core skills and competences as well as more locally developed learning needs. The report points to different Interest driven and destination driven learning pathways – destination driven meaning learning for employment. This seems to us too binary a division. Interest driven learning can often lead to skills for employment and vice versa. In reality people often cross over between different pathways.
Dense networks and relationships are seen to be central to the development of CofL with “anchor organisations” and “influential change makers” acting as “network hubs and stewards.” Three key factors are identified for developing CofL initiatives – leadership, networks and platform.
Although stressing the importance of networks and of community organisations, the examples provided seem to be driven by city governments. And the report also provides the example of a large employers overhauling their recruitment policy as driving change through their supply network, but there is no discussion of the importance of Small and Medium Enterprises who provide the majority of employment in cities like Valencia.
Cities are of course important but I do not see why the approach to learning in place based networks should not also include more dispersed population areas, including rural areas and towns in the south Wales valleys with different population structures.
One thing definitely welcome is that the technology plays an enabling function, supporting learning. Technology Enhanced Learning may have a weak link to place, but place is key to practice in learning.
Less welcome is the unnecessary emphasis on CofL as disruptive or as they call it a “quiet disruption.” Neither do I see Open Badges as a “disruption.” I can only see CofL and Open Badges as developing and extending traditional ideas of adult education.
The report also claims that CoFL challenges the fragmented rigid and centralised nature of public services. Certainly, education services have become fragmented but the major challenge is not that but is government austerity policies which have decimated adult education provision.
However, despite this, City of Learning is an exciting vision, and one I think which could spread beyond the RSA sponsored experiments and networks.
 The UK Centre for Cities has been undertaking a lot of interesting research on the future of cities. In a recent article on their website, they look at ‘why place matters when thinking about productivity. Productivity has been persistently low in the UK and the article discusses “‘Place’, one of the pillars of productivity identified by the
The UK Centre for Cities has been undertaking a lot of interesting research on the future of cities. In a recent article on their website, they look at ‘why place matters when thinking about productivity. Productivity has been persistently low in the UK and the article discusses “‘Place’, one of the pillars of productivity identified by the  Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the
Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the