Remembering Kerstin Engraf
Earlier this week we received the sad news that Kerstin Engraf, our friend and colleague from the Learning Layers project, had passed away. This was very shocking to us, because we had always learned to know her as a very lively and energetic person and we were expecting her to keep healthy. None of us could have expected this to happen. Below I try to summarise some of my memories of her in a nutshell.
Rembering Kerstin as a key actor in developing continuing vocational training at Bau-ABC Rostrup
We (researchers of ITB, University of Bremen) learned to know Kerstin Engraf at the beginning of the Learning Layers (LL) project when Bau-ABC Rostrup, the North-German training centre of construction centre joined in the project as an application partner. During the project most of our work focused on the apprentice training that was managed by full-time trainers (Lehrwerkmeister) and coordinated in Bau-ABC by Melanie Campbell. However, Kerstin, as the head of continuing training (CVT) of Bau-ABC, was interested in being involved in the development work and participated throughout the lifetime of the project. Moreover, she was supporting the launch of a follow-up project that focused on developing digital tools for training and learning in the CVT schemes of Bau-ABC. During this period we came to understand the complexity of the CVT schemes and the management of the sets short-term courses provided by external lecturers and trainers. And we realised that Kerstin had a complete overview and she knew how to manage the system through and through.
Remembering Kerstin as a contributor to the Construction pilot of the LL project
Looking back, I remember that Kerstin was keenly interested initial workshops with which we started to give shape for the Construction pilot activities. At the earliest phase we discussed the prospect of developing a digitized version of the “White Folder” of the apprentices of Bau-ABC. In these discussions we learned a lot, what the trainers expected of the digital support for a culture of action-oriented learning and self-organised learning. These ideas were taken on board, when the co-design work started to shape the Learning Toolbox (LTB) as a digital toolset to support working and learning processes in the construction sector.
Once the design idea had got its shape, Kerstin was eagerly promoting the idea at special events of construction professionals. I still remember her active support for the LL project activities at the national conference of well-builders and borehole builders (Brunnenbauertage) at Bau-ABC in May 2014 and at the North-German trade fair Nordbau in August 2014. In between we had had the LL project consortium meeting at Bau-ABC. Alongside the meeting we had a demonstration space for Bau-ABC apprentices and trainers. At each corner of the meeting room we had demonstration tables with laptops or tablet PCs to present particular digital tools, toolsets and platforms that we were developing. Thanks to Kerstin’s organisational talent we could manage a carrousel event in which over 100 apprentices and trainers rotated through each demonstration table as small groups whilst members of project team presented briefly the work with the tools.
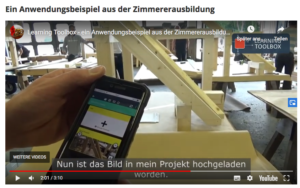
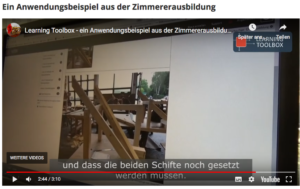
A very special contribution to the project was the preparation of the Bau-ABC videos (August-September 2014). These were designed give the project consortium an idea, what the trainers and apprentices were expecting of working and learning with the Learning Toolbox. This was of vital importance, since the design work was at a very early stage and the we only had a mock-up version of the toolset to be programmed. In the production of these videos Kerstin was eagerly involved and demonstrated her enthusiasm when editing the videos. Below you see exemplary video that presents the work with trainers’ blogs (predecessors of Learning Toolbox stacks). Here the handwriting of Kerstin is clearly visible (the speed and the music).
Later on, Kerstin was actively involved in developing and implementing a new kind of training concept – the Theme Room training – for all training staff of Bau-ABC. The idea came from the trainers themselves and they had already discussed some key principles, how to put it into practice. Kerstin and Melanie Campbell brought this into discussion in the LL project and it was implemented as a local training campaign during November 2015. The aim was to provide all Bau-ABC trainers basic multimedia competences with focus on vocational learning. The training was run by a pair of peer tutors (one from the trainers and one from the researchers). The training was shaped for four themes (that were covered by respective digital learning space) and the training took place on Friday afternoons. Kerstin was involved in the planning but chose to take the role of learner – and enjoyed it greatly.
Remembering Kerstin as a participant in the consortium meetings
Because of her primary duties Kerstin was not always able to participate in the transnational consortium meetings. But when she had the opportunity, she was very present in many ways. In particular she was actively covering the meetings with photos that were uploaded into the Facebook group “Learning Layers”. And she was also interested in covering the social and natural environments of the meeting venues. Some of these photos she shared on her Facebook page. Thus, we can refresh our memories of the meetings, the sites and extra-curricular activities in Graz, Innsbruck, Tallinn and Espoo. And of course, the project consortium meeting at Bau-ABC Rostrup and the social events at the nearby Bad Zwischenahn (including the lake cruise on the Zwischenahner Meer) were highlights to her and to all of us (as the photo below shows).
These memories have only been glimpses to the time when we worked together and to the activities that we carried out together. I hope that they have given a picture of a friend and colleague whom we learned to appreciate. Kerstin has gone but the work that we have done bears fruit and the good memories bring us forward.
Rest in peace, Kerstin!