Productive project meeting in Athens – Part Two: Common themes and working perspectives between two TACCLE projects
In my previous post I reported on my participation as a guest in the project meeting of the TACCLE VET project. As I mentioned, this project focuses on promoting digital competences in the field of vocational education and training (VET). The parallel project TACCLE 4 CPD (in which I am working) is developing models of continuing professional development (CPD) for different educational sectors. My task is to analyse and develop CPD models that are appropriate for the field of VET. As I have reported in my previous post, we found a lot of common points of interest and working perspectives. In this post I will have a closer look at the common themes and working interfaces.
Critical interpretation of the European DigCompEdu framework
The proposal for the TACCLE VET project had given a major role for the DigCompEdu framework and stated that the project seeks to extend it to the field of VET. The policy analyses of the TACCLE 4 CPD provided a somewhat more critical interpretation of the DigCompEdu framework. During the discussion the following points were made:
- In general we all appreciated the framework and its integrative approach to bring together teachers’/trainers’ professional competences, digital competences and pedagogic competences – in order to empower learners.
- We also appreciated the approach to develop a progression model for promoting digital competences and to formulate proficiency statements for different competence areas and levels.
- However, the framework tends to focus on educational subjects or academic disciplines and take the digital competences as add-on aspects for enriching pedagogy and subject-based learning. Moreover, the progression ladder tends to atomize the promotion of competences.
- Concerning VET it is important to take into account developments in working life and in education/training to create an appropriate picture on the needs for promoting digital competences.
- Concerning VET providers it is essential to focus on holistic solutions for promoting digital competences in specific occupational fields and at the level of the whole organisation.
Consequently, the idea of ‘extension’ of the framework required also critical interpretation and adaptation in the light of specific requirements and working perspectives for the field of VET. Yet, as mentioned in the previous post, the competence areas andthe proficiency statements provide an essential basis for developing evaluation tools. Below I try to recapitulate my points that outline, how to proceed with such adaptation.
Digital transformation and digitization as challenges for VET
A major point to be considered in the field of VET is to observe the two parallel processes:
- The ‘digital transformation’ has an impact across work organisations, production processes, supply networks and service networks. These macro-level developments provide challenges for the role of skilled workers and for the redistribution of working and learning opportunities.
- The ‘digitization’ at the level of working and learning tasks has an impact on the prospects of vocational learners to respond and to contribute to the macro-processes that have been mentioned above. However, this varies in different occupational fields and in different education/training contexts.
Innovation paths for promoting digital competences in VET
The set innovation paths that I had outlined in my research paper for ECER 2019 – and then as an adapted version in my presentation for the Athens meeting – try to take the above-mentioned processes and different VET domains into consideraration. Below I will summarise the paths and their key characteristics briefly:
- The “CARO path” refers to use of digital learning spaces to support interactive learning in nursing education and across the whole curriculum. This path stands for ‘whole curriculum’ solutions and for sensitive learning contexts.
- The “Learning Toolbox path” refers to use of an integrative digital toolset to support project-based training and learning in VET. This path stands for the introduction of flexible toolsets that promote transparency and awareness of structures learning processes.
- The “innowas path” refers to introduction of specific digital tools or software solutions to enhance the learners’ awareness of their experiential learning and/or to make transparent the hitherto non-transparent work processes.
- The “smart OER users’ path” refers to initiatives in the field of VET that combine the use of OER, related digital tools and open access materials in the shaping of creative learning environments.
As I have mentioned in my previous post, the innovation paths were taken into account when the TACCLE VET partners extended their list of possible learning scenarios and related OER solutions.
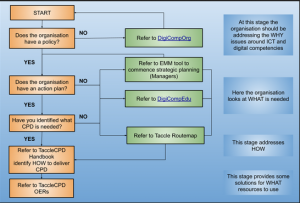
The Routemap document as a strategic tool
Finally, it is worthwhile to note that the Routemap tool (that is being developed in the TACCLE 4 CPD project) has shifted the emphasis from the digital competences of individual learners to the ICT capability across the organisation. Also, it has aggregated the set of competence level to fewer levels – initial, e-enabled, e-confident, e-mature. Furthermore, the tool has formulated organisational proficiency statements for the organisational planning – how to enhance the ICT capability – and for the related training measures – what level do we want to reach.
—
I think this is enough of the Athens meeting and on the ideas and further thoughts that we shared. Now it is time to work further to make the best out of both projects working together.
More blogs to come …